- Legend
- Added
- Deleted
1. Introduction
This document describes the RIPE Policy Development Process (RIPE PDP), outlining how policies relating to the operation of the Internet are developed by and for the RIPE community. The RIPE Chair is the author and owner of this document.
Since its creation in 1989, RIPE has been a forum for people to decide on common practices. These common practices may come in different forms and/or under different names:
- Best common practice (BCP)
- Recommendations and guidelines to the community
- Recommendations and guidelines to the RIPE NCC
- Policy
This document refers solely to “Policy”.
The process that results in the creation of a policy has some important and fundamental principles:
- It is open to all and follows an established, bottom-up process of collaboration. Everyone interested in the well-being of the Internet may propose a policy and take part in the discussions that follow on from the proposal.
- It is transparent. All discussions and resulting actions are documented and freely available to all.
- Conclusions are reached by consensus.
- All policies are documented within RIPE Documents and placed in the RIPE Document Store.
The policies referred to in this document are those developed through the bottom-up RIPE PDP. This document does not describe the specific administrative or technical procedures established in order for a policy to be applied. Depending on the specifics of a policy, procedures can be set by the Local Internet Registries (LIRs), End Users and the RIPE NCC as required. These procedures must conform to all policies that are in place.
RIPE Policies are also separate from RIPE NCC business practices and procedures. Business practices and procedures that the RIPE NCC follows are defined and governed by the RIPE NCC Executive Board and approved by the RIPE NCC membership. If a policy proposal would bring implementation and/or operational problems for the RIPE NCC if accepted, the RIPE NCC Executive Board is tasked to notify the RIPE community accordingly as well as to make necessary suggestions and recommendations about possible changes to the proposal.
2. The Process
The process of developing a policy has four distinct phases:
1. Creating a Proposal
2. Discussion Phase
3. Review Phase
4. Concluding Phase
These four phases are detailed below with timelines. They are proposed deadlines for the various stages. These may be varied for individual proposals, but the actual timescales must be documented.
In all phases of the RIPE PDP, suggestions for changes to the proposal and objections regarding the proposal must be justified with supporting arguments.
In this process, the RIPE NCC (the RIPE community's secretariat) gives administrative support by:
- Publishing proposals and related discussions on relevant webpages
- Tracking deadlines
- Making announcements to the RIPE community
- Providing assistance in drafting policy proposals if requested
- Providing relevant facts and statistics
- Publishing an impact analysis that points to the possible effects of the proposed policy and the work that would be involved in its implementation.
The process flow is illustrated in a diagram, attached as Appendix A.
There are a number of points in the PDP at which disputes could arise. The PDP is designed so that compromises can be made and genuine consensus achieved. However, there are times when even the most reasonable and knowledgeable people are unable to agree on the decisions made at the end of any PDP phase. To achieve the goals of openness, transparency and fairness, such conflicts must be resolved through a process of open review and discussion.
2.1 Creating a Proposal
Discussions may be started by anyone at any time. Participants are welcome to discuss broad ideas as well as to make detailed policy proposals. Proposals are made using the Policy Proposal template, attached as Appendix B.
The template forms a structure for the proposal. It details the reason for the proposal and any perceived consequences of the proposal.
A proposal is discussed publicly in the relevant RIPE Working Group (WG)[1]. The proposal is usually submitted via the chair of that WG. If the proposer [2] is not certain which WG is appropriate for discussion of the proposal, they can send the proposal to the RIPE Chair at policy-proposal@ripe.net. In some cases, a proposal may need more than one WG's input. In such cases, before the proposal is published, the relevant WG chairs will discuss the situation and decide the WG most suited to discussion of the proposal. Necessary announcements will be made to the other WG(s) so they can follow the discussions.
The RIPE NCC gives each proposal its own unique identifier and publishes it on a dedicated RIPE webpage. This webpage contains the version history and the status of all proposals. A proposal can have one of the following statuses at any given time:
- Open for Discussion: Meaning that the proposal is still being discussed within the RIPE PDP.
- Accepted: Meaning that the RIPE community accepted the proposal after all stages of the RIPE PDP were completed.
- Withdrawn: Meaning that the proposal is withdrawn either by the proposer or by the WG chairs at one of the decision-making points.
2.2 Discussion Phase
At the end of the Discussion Phase, the proposer, with the agreement of the WG chair, decides whether the proposal will move to the next phase (Review Phase) or if it should be withdrawn from the RIPE PDP, depending on the feedback received. This should be done no more than four weeks after the end of the Discussion Phase. If the proposer does not communicate this decision to the WG chair within four weeks, the WG chair can withdraw the proposal due to lack of response from the proposer.
If significant comments or changes are suggested during the Discussion Phase, the proposer will edit the proposal and the new version of the proposal will be published. A new Discussion Phase will then start for the new version of the proposal.
If the suggested comments and changes are not so significant to require a new Discussion Phase, the proposer and WG chair can decide to move the proposal to the next phase (Review Phase) with a new version of the proposal incorporating the necessary edits.
Each version of the proposal is publicly archived to transparently show the history of changes to the proposal.
If the proposer decides to take the proposal to the next phase, the draft RIPE Document should be prepared within four weeks. A policy proposal can result in the modification of an existing RIPE Document or can result in publication of a completely new RIPE Document. If the proposal is a modification of an existing policy or it is a new policy that needs to be documented in an existing RIPE Document, then a draft RIPE Document clearly pointing to the changes to the existing document will be published. If the proposal requires a completely new RIPE Document to be published, the draft should be produced before the proposal can be moved to the Review Phase.
The RIPE NCC will also conduct and publish an impact analysis about the proposal before it can be moved to the Review Phase. The goal of this analysis is to provide relevant supporting information to facilitate the discussions about the proposal and provide some projections about the possible impact if it were to be accepted. This analysis will contain the following points:
- The RIPE NCC's understanding of the proposed policy
- Impact on the registry and addressing systems (including Internet resource consumption, aggregation and fragmentation)
- Impact on RIPE NCC operations/services
- Legal impact
2.3 Review Phase
The purpose of the Review phase is to review the full draft RIPE Document compiled at the end of the Discussion Phase so that the final documentation the proposal will lead to and all modifications made to that document are transparent to the community. During the Review Phase, discussion of the proposal can continue, also in the light of the impact analysis that is published at the beginning of this phase, and within the context of the proposal, further modifications can still be suggested regarding the draft RIPE Document. The Review Phase should last for a maximum of four weeks.
At the end of the Review Phase, the WG chair determines whether the WG has reached rough consensus. If the WG chair decides that consensus has not been reached, then the WG chair can withdraw the proposal. Alternatively, the WG chair can send can:Send the proposal back to the Discussion Phase if the proposer is willing to continue to author the proposal and make the necessary changes to the proposal according to the feedback received from the community. The WG chair can also decide Decide to have the draft RIPE Document edited and start a new Review Phase with a new version of the proposal.
2.4 Concluding Phase
If the WG chair determines that the WG has reached consensus at the end of the Review Phase, the WG chair moves the proposal to a "Last Call for Comments" and the Concluding Phase starts. The Last Call period lasts four weeks. The Last Call announcement is also posted to the WG mailing list and to the Policy Announce Mailing List (policy-announce@ripe.net).
The purpose of this Last Call period is to provide the community with a final opportunity to comment on the proposal. This is mainly intended for those who missed the previous two phases and want to oppose the proposal. It gives time to the community after the relevant WG chair declares rough consensus at the end of the Review Phase so that suggestions for any final changes or objections to the proposal can be sent to the WG mailing list. At this stage, objections need to be justified just as in the other phases for them to be taken into account.
At the end of the Last Call period, the WG chair will evaluate the feedback received during this period and decide whether consensus has been achieved. If there is no feedback from the community at this stage, this is likely to be regarded as consensus and it will mean the previous call of rough consensus from the WG chair at the end of the Review Phase still holds.
If consensus has been achieved, the RIPE NCC will announce the decision of the WG chair and, if necessary, implement the policy.
If consensus has not been achieved, the WG chair can decide to either withdraw the proposal or send it back to one of the previous phases. The proposer (or anyone else) is free to return the proposal to the WG for further discussion after a withdrawal.
3. Appealable Actions
3.1 Discussion Phase
During the Discussion Phase, anyone who has a complaint or other concern about the policy proposal or how it is being handled in the WG should first raise the matter with the chair of that WG. If the dispute cannot be resolved with the WG chair, the Appeals Procedure can be invoked.
3.2 Review & Concluding Phases
At these stages of the process – i.e. after the WG chair has declared initial consensus or the proposal is in Last Call – complaints should not be about the policy proposal itself unless there are exceptional extenuating circumstances.
Anyone who believes that the proposal has not been handled correctly or that the WG chair has made an incorrect determination of consensus should first raise the matter with the WG chair. If the dispute cannot be resolved with the WG chair, the Appeals Procedure can be invoked.
4. Appeals Procedure
If a grievance cannot be resolved with the chair of the WG the matter can be brought to the attention of the Working Group Chairs Collective (WGCC). Anyone may submit an appeal. This must be submitted to the relevant WG mailing list(s) and to the Policy Announce Mailing List (policy-announce@ripe.net). The appeal will also be published by the RIPE NCC at appropriate locations on the RIPE web site. Any appeal should include a detailed and specific description of the issues and clearly explain why the appeal was submitted. An appeal must be submitted no later than four weeks after the appealable action has occurred.
The WGCC will decide by consensus whether to uphold or reject appeals which have been submitted. The decision of the WGCC should be reached no later than four weeks of an appeal being made. Interested parties shall recuse themselves from any discussion or decision within the WGCC relating to the appeal.
If the dispute cannot be resolved by the decision of the WGCC, the issue should be brought to the RIPE Chair. The decision of the RIPE Chair will be final.
References
[1] The RIPE community has formed a number of working groups to deal with issues and topics affecting the Internet community. Every RIPE Working Group has at least one chair (some working groups may have co-chairs). They are responsible for chairing discussions in the working group and, where necessary, making decisions in the Policy Development Process.
Appendix A: Policy Development Process Diagram
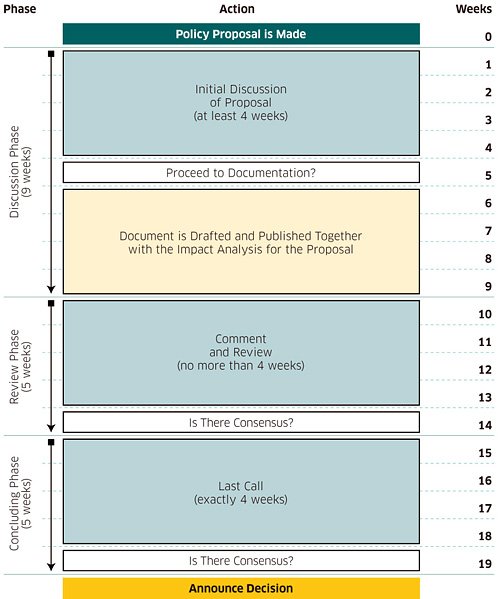
NOTE:The actual timelines of individual proposals may vary. They are documented and announced per proposal
Appendix B: Policy Proposal Template
1. Number (assigned by the RIPE NCC)
2.Policy Proposal Name
3.Author Details
a. name
b. email
c. organisation
4. Proposal Version (assigned by the RIPE NCC)
5. Submission Date
6. Suggested RIPE WG for discussion and publication
7. Proposal Type
a. new, modification or deletion
8. Policy Term
a. Temporary (time period)
b. Indefinite
9. Summary of Proposal
10. Policy Text
a. Current policy text (if modification)
b. New policy text
11.Rationale
a. Arguments supporting the proposal
b. Arguments opposing the proposal
Acknowledgements
This document was edited by Fergal Cunningham.
RIPE Working Group Chairs have reviewed and commented on the document before it was published.